
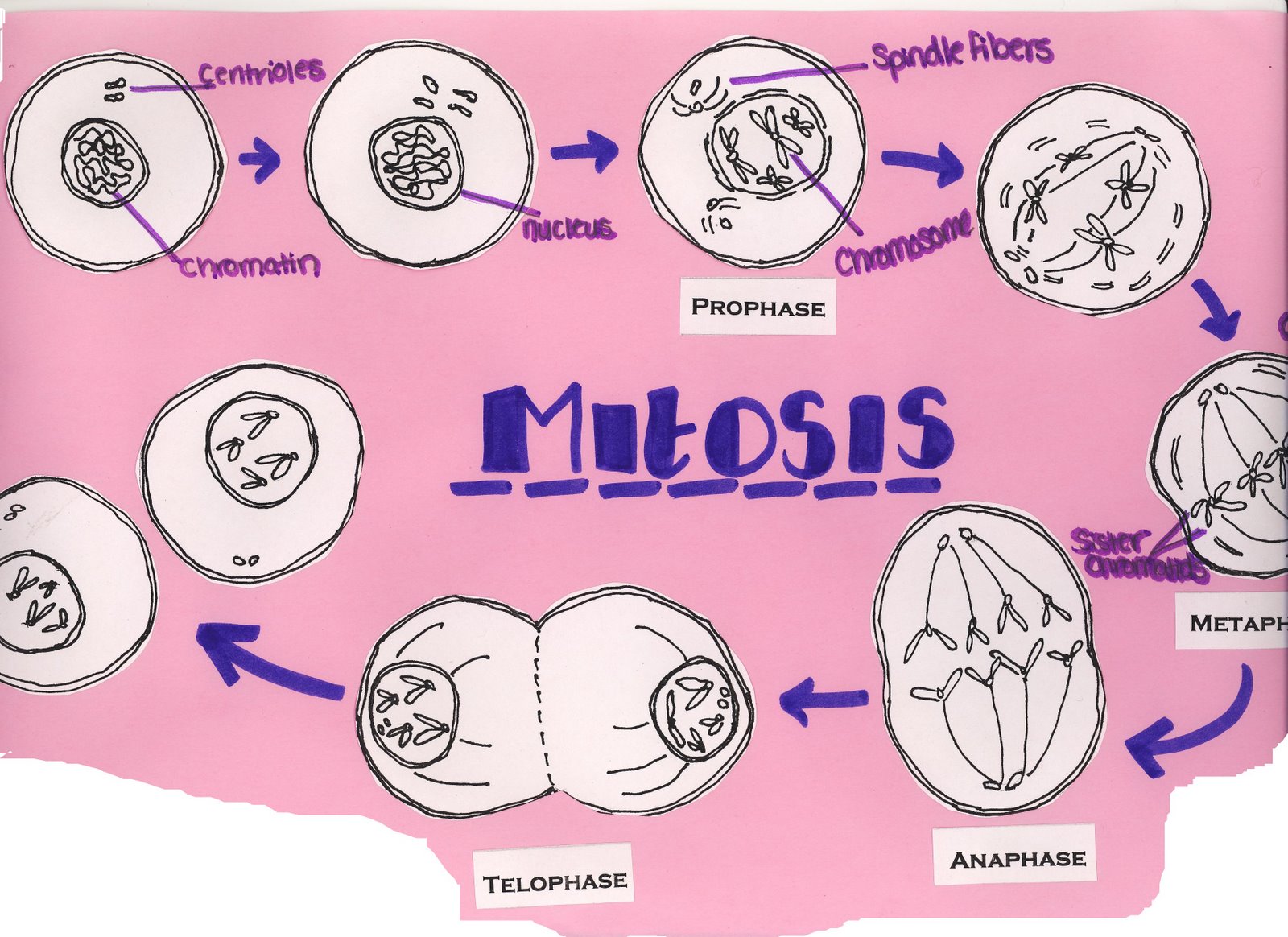
Metaphase 1: In this stage the chromatids line up in the center of the cell, and the spindle fibres attach to the chromatids.Prophase 1: In this stage the chromatids connect and cross over, this is when the chromatids trade sections.


They are referred to as daughter chromosomes. Once the paired sister chromatids separate from one another, each is considered a "full" chromosome.The paired centromeres in each distinct chromosome begin to move apart..During anaphase, the following key changes occur: Spindle fibers not connected to chromatids lengthen and elongate the cell. In anaphase, the paired chromosomes ( sister chromatids) separate and begin moving to opposite ends (poles) of the cell. The chromosomes begin to migrate toward the cell center.The kinetochore fibers "interact" with the spindle polar fibers connecting the kinetochores to the polar fibers.Kinetochores, which are specialized regions in the centromeres of chromosomes, attach to a type of microtubule called kinetochore fibers.Polar fibers, which are microtubules that make up the spindle fibers, reach from each cell pole to the cell's equator.The two pairs of centrioles (formed from the replication of one pair in Interphase) move away from one another toward opposite ends of the cell due to the lengthening of the microtubules that form between them.The mitotic spindle, composed of microtubules and proteins, forms in the cytoplasm.Chromatin fibers become coiled into chromosomes, with each chromosome having two chromatids joined at a centromere.During prophase, a number of important changes occur: Prophase (versus interphase) is the first true step of the mitotic process. The nuclear envelope breaks down and spindles form at opposite poles of the cell. In prophase, the chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
